Many homeowners have been able to eliminate the need for oil or gas to heat their homes by installing an air source heat pump system. When a heat pump is installed, the electricity use in your home will go up considerably, and your bill will show this rise in costs. If you have oil and gas heating at the moment, their costs will be eliminated altogether when you take the boiler out.
Why is the electric bill high with a heat pump?
Switching from gas or oil heating to an air source heat pump will increase your electricity bill, as is it powered by electricity. If your bill is considerably higher, it could be because of a lack of maintenance or even faults with the system. You should check for any error codes and how you are using the system.

How much electricity do heat pumps use?
Heat pumps do require some electricity to run, but the amount they produce exceeds by 3 or 4 times the amount they use. This makes it a CoP of 3 or 4. CoP is used to calculate a heat pump’s efficiency. With one unit of electricity currently costing 30.0p per kWh a typical home using 12000 kwh per year would make your heat pump operating cost of £900.
Although you are getting heat free from the air with a heat pump, it needs electricity to run and convert the energy.
CoP is used to calculate a heat pump’s efficiency. This unit is calculated by calculating the amount of energy input into it (electricity) and the amount of energy that is output out of it in the form of heat. A heat pump with a CoP of three can generate three kW of heat for every kW of electricity consumed.
Heat pumps can have different efficiencies at different times of the year. Factors such as the size of your home, how well it is insulated, and how much hot water you use will all determine the effectiveness of your heat pump.
You can find out more on air source heat pump efficiencies in this guide from the Energy Saving Trust.

Heat pump faults that cause a high electricity bill
- The outdoor unit has debris stuck in it.
- The compressor isn’t running properly.
- Errors with the temperature sensors.
- The unit needs cleaning or servicing.
- Leaks in the ducting.
- Faulty or wrongly configured reversing valve.
- Fault with the indoor or outdoor heat exchanger.
How to lower your electric bill with a heat pump?
Although switching to a heat pump will likely lower your energy bills, it will increase your electricity usage. There are several steps that can be taken to reduce your electricity bill.

Don’t switch off the heat pump
First, leave the heat pump running all the time. This may sound like the bills will inevitably be high, but when the unit is on all the time, it can calculate the most efficient amount of heat to produce night and day. If you switch it off at any time, it consumes more electricity to start up again and find the best efficiency.
Try to avoid constantly adjusting the temperature. The heat pump will use more power if you frequently adjust the temperature depending on how warm or cold you are. When it maintains the same temperature, it will use less power. Set the thermostat to a specific temperature and leave it alone.

Check if the immersion heating keeps turning on
If your electricity bill unexpectedly rises, it could be because your immersion heater is being used for extended periods of time – the most expensive way to heat your home and hot water. Immersion heaters are part of a heat pump system to provide extra heat when required.
If the temperature of the water is set too high, your heat pump will have to work harder to heat the water, so may need to use the immersion heater which runs on the electricity mains.

Cool the water temperature
Heat pumps can still keep the house warm if you cool the water temperature to 40 degrees Celsius or less. This will be enough to heat your home efficiently.
Keeping track of your electricity consumption is essential for understanding how your heat pump performs throughout the year. We recommend keeping a monthly record of electricity usage.
You will then be able to build up a picture of how it is performing over time and see if any major discrepancies emerge. Compare this to previous year’s usage, both electricity and gas heating.
Check for cheaper electricity tariffs
Shop around for lower tariffs with your current or another supplier. Don’t be afraid to switch supplier, especially if you know your demand will be high. Keep an eye out for the standing charge, which is listed separately but can add over £100 on your annual bill. Once you know what your usage is likely to be, comparisons can be simple.
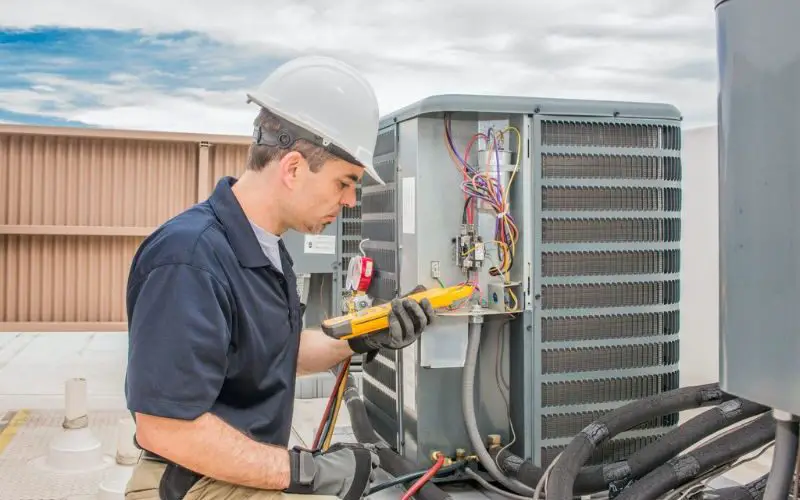

Service the heat pump each year
Heat pumps require maintenance and this should be done once a year, best done before the heating season. A poorly maintained unit can consume up to 25% extra electricity.
Dirt and dust can build up in heat pump components such as filters and the fan to reduce the amount of airflow that can pass through the system.
Heat pumps may also need to be serviced annually to keep the warranty valid, so make sure to keep up with it.
For more technical information on air source heat pumps, visit the Heat Pumps website.
Use solar panels to power the heat pump
Heat pumps can be used in conjunction with solar PV panels. You could reduce your energy bills while also lowering your carbon footprint if you use electricity generated on-site.
It is estimated that using solar PV panels could cut your heat pump’s operating costs by up to 40%. Although installing solar PV panels is an investment, you will most likely recoup your investment within a few years.
You can find out more about heat pump running costs in this article from The Guardian newspaper.
Summary
These are some of the ways to reduce electricity costs with a heat pump:
- Reduce heat loss through windows. Install double or even triple glazing.
- Reduce heat loss through walls and lofts. Install loft and cavity wall insulation.
- Monitor your heat pump usage monthly.
- Use the heat pump with underfloor heating or larger-sized radiators.
- Look for cheaper energy tariffs.
- Service the ASHP annually.
- Install Solar PV to power the heat pump.
Read related articles:
