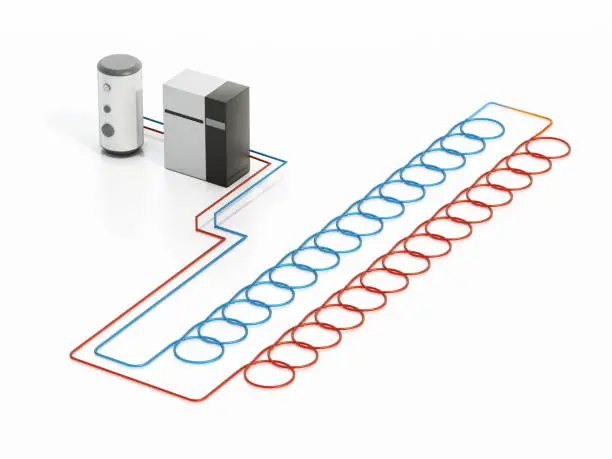
If you’re looking for an energy-efficient way to heat your home, you might be interested in ground source heat pumps. These systems work by harnessing the natural heat stored in the ground to provide warmth to your home. Unlike traditional heating systems that burn fuel to create heat, ground source heat pumps use electricity to move heat from one place to another, making them a more sustainable option.
So, how do ground source heat pumps work? Essentially, they use a network of pipes buried in the ground to extract heat, which is then transferred to a refrigerant fluid. This fluid is then compressed, which raises its temperature even further, before it is used to heat your home. In the summer, the process can be reversed, with the heat pump extracting heat from your home and transferring it back into the ground to provide cooling.
What is a Ground Heat Pump?
If you’re looking for an energy-efficient way to heat your home, a ground heat pump could be the answer. A ground heat pump is a type of heating and cooling system that harnesses the energy stored in the ground to regulate the temperature of your home. They’re becoming increasingly popular as people look for ways to reduce their carbon footprint and save money on energy bills.
How Does a Ground Heat Pump Work?
A ground heat pump works by extracting heat from the ground and using it to heat your home. The process starts with a network of pipes that are buried in the ground. These pipes are filled with a mixture of water and antifreeze, which absorbs the heat from the ground. The heated liquid is then pumped into a heat exchanger, where the heat is transferred to the refrigerant in the heat pump.
The refrigerant is then compressed, which raises its temperature. The hot refrigerant is then passed through a coil in your home’s heating system, where it releases its heat into the air. The cooled refrigerant is then passed back through the heat exchanger, where it absorbs more heat from the ground and the process starts again.
Types of Ground Heat Pumps
There are two main types of ground heat pumps: closed-loop and open-loop systems. Closed-loop systems are the most common type of ground heat pump. They use a network of pipes filled with water and antifreeze that are buried in the ground. The liquid in the pipes absorbs the heat from the ground and is then pumped into the heat exchanger of the heat pump.
Open-loop systems, on the other hand, use water from a well or other source as the heat exchange fluid. The water is pumped into the heat exchanger, where it releases its heat into the refrigerant. The cooled water is then returned to the source.
Both types of ground heat pumps have their advantages and disadvantages, and the best type for your home will depend on a number of factors, including the size of your property and the soil conditions.
Ground Heat Pump Components
Heat Exchanger
The heat exchanger is the component of a ground heat pump that extracts heat from the ground and transfers it to the refrigerant. There are two types of heat exchangers: closed-loop and open-loop. Closed-loop heat exchangers use a network of pipes filled with a heat transfer fluid that is circulated through the ground and back into the heat pump. Open-loop heat exchangers use water from a well or surface body of water as the heat transfer fluid.
Compressor
The compressor is responsible for compressing the refrigerant gas to increase its temperature. This process is necessary to transfer heat from the ground to the heat pump’s refrigerant. The compressor is the most energy-intensive component of a ground heat pump, and its efficiency is a key factor in the overall efficiency of the system.
Expansion Valve
The expansion valve is a small component that regulates the flow of refrigerant through the system. It is located between the compressor and the heat exchanger and is responsible for reducing the pressure and temperature of the refrigerant before it enters the heat exchanger. This process allows the refrigerant to absorb heat from the ground.
Refrigerant
The refrigerant is the fluid that circulates through the heat pump and is responsible for transferring heat from the ground to the indoor air. The refrigerant is a critical component of the system, and its properties determine the efficiency and performance of the heat pump. The most common refrigerant used in ground heat pumps is R-410A, which is an environmentally friendly and efficient refrigerant. Overall, a ground heat pump system is a reliable and efficient way to heat and cool your home. By understanding the components of the system, you can make informed decisions about the installation and maintenance of your ground heat pump.
Installation of Ground Heat Pumps
Installing a ground heat pump system involves several steps that need to be carefully planned and executed. In this section, we will discuss the key aspects of installing a ground heat pump system, including sizing the system, designing the ground loop, and the installation process.
Sizing a Ground Heat Pump System
The first step in installing a ground heat pump system is to determine the appropriate size for your home. This involves calculating the heat load of your home, which takes into account factors such as the size of your home, the number of occupants, the insulation, and the local climate. A qualified installer can help you determine the appropriate size for your home.
Ground Loop Design
The ground loop is a critical component of a ground heat pump system. It consists of a series of pipes that are buried in the ground and filled with a heat transfer fluid. The ground loop absorbs heat from the ground during the winter and releases heat back into the ground during the summer. The design of the ground loop depends on several factors, including the soil type, the size of the system, and the local climate. A qualified installer can help you design the ground loop that is best suited for your home.
Installation Process
The installation process for a ground heat pump system typically involves several steps. First, the ground loop is installed in the ground. This may involve digging trenches or drilling boreholes, depending on the design of the ground loop. Next, the heat pump unit is installed in your home. This may involve connecting the heat pump to your existing ductwork or installing new ductwork. Finally, the system is tested to ensure that it is working properly. A qualified installer can help you through each step of the installation process.
How much does a ground source heat pump cost?
Generally, a ground source heat pump system can cost anywhere between £10,000 to £20,000, with larger or more complex systems costing more. However, it’s important to keep in mind that while the initial cost may seem high, the long-term savings on energy bills can make it a worthwhile investment.
In addition to the initial cost of the system, there are also ongoing costs to consider such as maintenance and repairs. It’s important to work with a reputable installer who can provide you with a detailed breakdown of all costs associated with the installation and maintenance of your ground source heat pump system. With proper installation and maintenance, a ground source heat pump can provide a reliable and cost-effective source of heating for your home or business for many years to come.
Benefits of Ground Heat Pumps
If you’re considering installing a ground heat pump, there are several benefits that you should be aware of. In this section, we’ll cover the energy efficiency, environmental benefits, and cost savings that come with using ground heat pumps in your home.
Energy Efficiency
One of the primary benefits of using a ground heat pump is the high level of energy efficiency it provides. Ground heat pumps can achieve an efficiency rating of up to 600%, which means that for every unit of electricity used to power the system, you’ll get six units of heat in return. This level of efficiency is achieved by using the constant temperature of the ground to heat or cool your home, rather than relying on fossil fuels or electricity to generate heat.
Environmental Benefits
Ground heat pumps are also an environmentally friendly choice for heating and cooling your home. They produce no emissions, which means that they don’t contribute to air pollution or greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, because they rely on the constant temperature of the ground, they don’t deplete natural resources or contribute to the extraction of fossil fuels.
Cost Savings
Another benefit of using a ground heat pump is the potential for cost savings. While the upfront cost of installing a ground heat pump can be higher than other heating and cooling systems, the long-term savings can be significant. Because ground heat pumps are so energy efficient, they can help you save money on your energy bills over time. Additionally, ground heat pumps require less maintenance than other heating and cooling systems, which can also save you money in the long run.
Overall, if you’re looking for an energy-efficient, environmentally friendly, and cost-effective way to heat and cool your home, a ground heat pump may be the right choice for you.
Will a heat pump save me money on my energy bill?
Because they don’t generate heat like traditional heating systems, they can be much more energy-efficient, resulting in lower energy bills. In addition, many heat pumps are equipped with smart technology that can help you optimize your energy usage and save even more money.
However, the amount of money you can save with a heat pump depends on a variety of factors, such as the size of your property, the climate in your area, and the efficiency of your heat pump system. It’s important to work with a reputable installer who can help you choose the right size and type of heat pump for your property, as well as provide you with information on how to properly maintain and use your system to maximize energy savings.
Maintenance of Ground Heat Pumps
Ground source heat pumps (GSHPs) are a reliable and efficient way to heat and cool your home. With regular maintenance, you can ensure that your GSHP system continues to operate effectively and efficiently for many years. Here are some tips to keep your GSHP system running smoothly:
Regular Maintenance
Regular maintenance of your GSHP system is essential to ensure its efficient operation. Here are some maintenance tasks you should perform regularly:
- Check the air filters every three months and replace them if they are dirty.
- Clean the outdoor unit regularly to remove any debris or dirt that may have accumulated on the coils.
- Check the water pressure and temperature gauges regularly to ensure they are within the recommended range.
- Inspect the ductwork for any leaks or damage and repair as necessary.
- Have a professional technician inspect and service your GSHP system once a year.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Even with regular maintenance, you may encounter some issues with your GSHP system. Here are some common issues and how to troubleshoot them:
| Issue | Troubleshooting |
|---|---|
| No Heat/Cooling | Check the thermostat settings and make sure it is set to the correct temperature. Check the circuit breaker and ensure it is not tripped. Check the air filters and clean or replace as necessary. If the issue persists, contact a professional technician. |
| Low Water Flow | Check the water pressure gauge and make sure it is within the recommended range. Check for any leaks or damage in the ductwork and repair as necessary. If the issue persists, contact a professional technician. |
| Strange Noises | Check the outdoor unit and remove any debris or dirt that may have accumulated on the coils. Check the ductwork for any leaks or damage and repair as necessary. If the issue persists, contact a professional technician. |
By following these maintenance tips and troubleshooting common issues, you can ensure that your GSHP system continues to operate efficiently and effectively, providing you with reliable heating and cooling for many years.
